If you’re looking for a powerful and free Integrated Development Environment (IDE) to create desktop applications with a graphical user interface, Lazarus is a great choice. Lazarus is based on the Free Pascal Compiler and provides a Delphi-like development experience, complete with a drag-and-drop form designer and support for cross-platform development. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the steps to install Lazarus on FunOS, so you can start building native applications for Linux and beyond.
What is Lazarus?
Lazarus is a free and open-source IDE for Rapid Application Development (RAD) using the Free Pascal programming language. It is fully compatible with Delphi and offers a familiar environment for developers who have used Delphi in the past. Lazarus includes a powerful form designer, code editor, and a rich set of components that make it easy to create modern GUI applications.
With Lazarus, you can develop:
- File managers and image viewers
- Database and reporting tools
- Graphic and multimedia software
- Games and educational applications
- Cross-platform commercial software
Lazarus runs on Linux, Windows, macOS, and even Raspberry Pi, making it an excellent tool for developers targeting multiple platforms.
How to Install Lazarus on FunOS
Work on: 22.04.5 ✅ | 24.04.4 ✅ | 25.04 ✅ | 25.10 ✅ | 26.04 ✅
Follow these steps to install Lazarus on your FunOS system.
Step 1: Download the Lazarus .deb Files
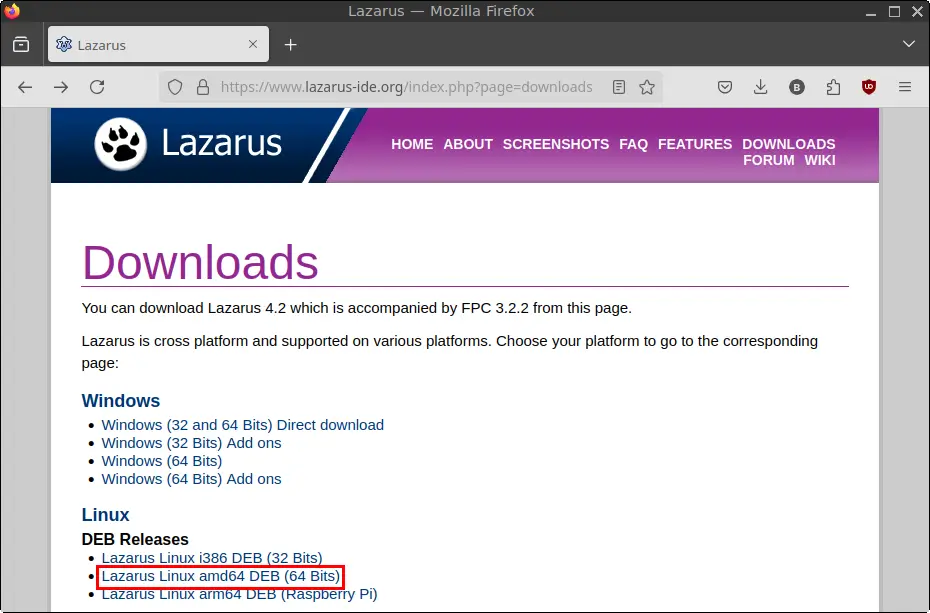
1. Open your web browser and go to the official Lazarus download page:
https://www.lazarus-ide.org/index.php?page=downloads
2. Scroll down to the Linux and DEB Releases section.
3. Click the link titled “Lazarus Linux amd64 DEB (64 Bits)”.
4. You will be redirected to SourceForge. Download the following three .deb packages:
lazarus-project_*.debfpc-src_*.debfpc-laz_*.deb
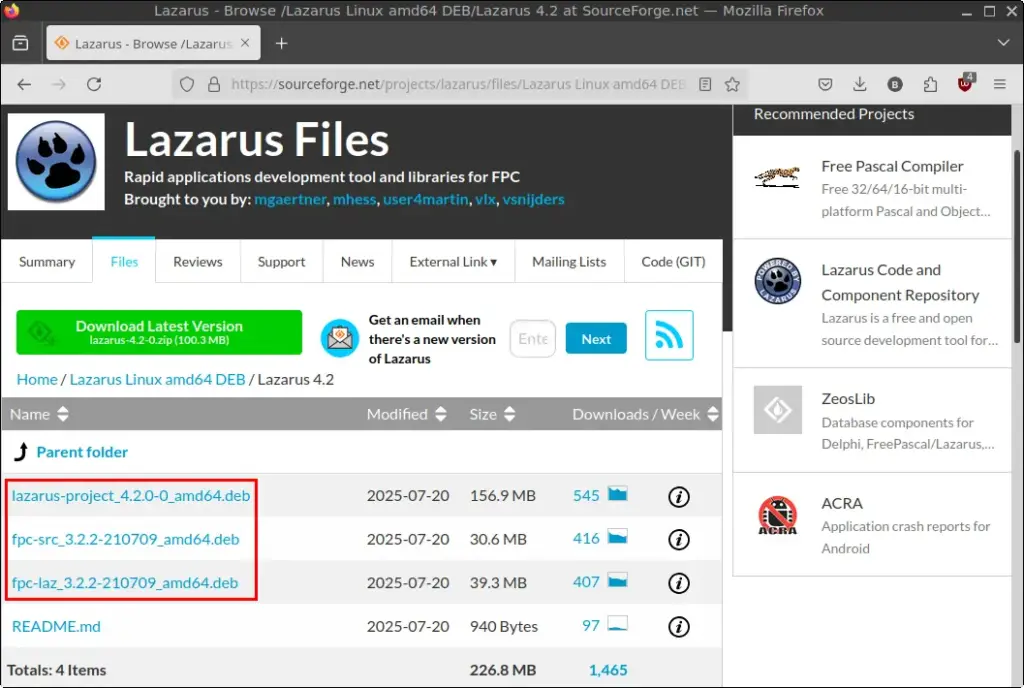
5. Save all three files in your Downloads directory.
Step 2: Open a Terminal
You can open a terminal in any of the following ways:
- Click Menu in the lower-left corner, then click Terminal
- Click the Terminal icon in the tray
- Press
Ctrl + Alt + Ton your keyboard
Step 3: Navigate to the Downloads Directory
In the terminal, type:
cd ~/DownloadsStep 4: Update the Package List
Run the following command to update the package list:
sudo apt updateStep 5: Install Lazarus
Now install the downloaded .deb files using the following command:
sudo apt install ./lazarus-project_*.deb ./fpc-src_*.deb ./fpc-laz_*.debThis command will install the Lazarus IDE, the Free Pascal Compiler, and the Free Pascal source files.
Step 6: Remove the Downloaded .deb Files (Optional)
If you want to save disk space, you can delete the .deb files after installation:
rm -f lazarus-project_*.deb fpc-src_*.deb fpc-laz_*.debStep 7: Reload the Menu
To ensure Lazarus appears in your application menu:
- Click the Menu button in the lower-left corner.
- Click Reload menu.
Launching Lazarus
To start Lazarus:
- Click the Menu button
- Go to the Development category
- Click Lazarus
Lazarus will initialize and prompt you to set up its configuration. You can accept the defaults or customize them based on your needs.
How to Uninstall Lazarus on FunOS
If you ever want to remove Lazarus from your system, follow these steps:
Step 1: Open a Terminal
Same as before, use any of the three methods to open a terminal.
Step 2: Remove Lazarus
Run the following command:
sudo apt remove --purge lazarus-project fpc-src fpc-lazStep 3: Remove Unused Dependencies
After uninstalling, clean up any leftover packages:
sudo apt autoremove --purgeStep 4: Remove User Configuration Files (Optional)
To delete Lazarus configuration files stored in your home directory:
rm -rf $HOME/.lazarusStep 5: Reload the Menu
To update your application menu:
- Click the Menu button
- Click Reload menu
Conclusion
Lazarus is a powerful and flexible IDE that brings the Delphi-style development experience to the world of open source and cross-platform programming. By following the steps above, you can easily install Lazarus on FunOS and begin building modern desktop applications. Whether you’re a student, hobbyist, or professional developer, Lazarus offers the tools you need to build fast, native, and cross-platform applications with ease.

Leave a Reply